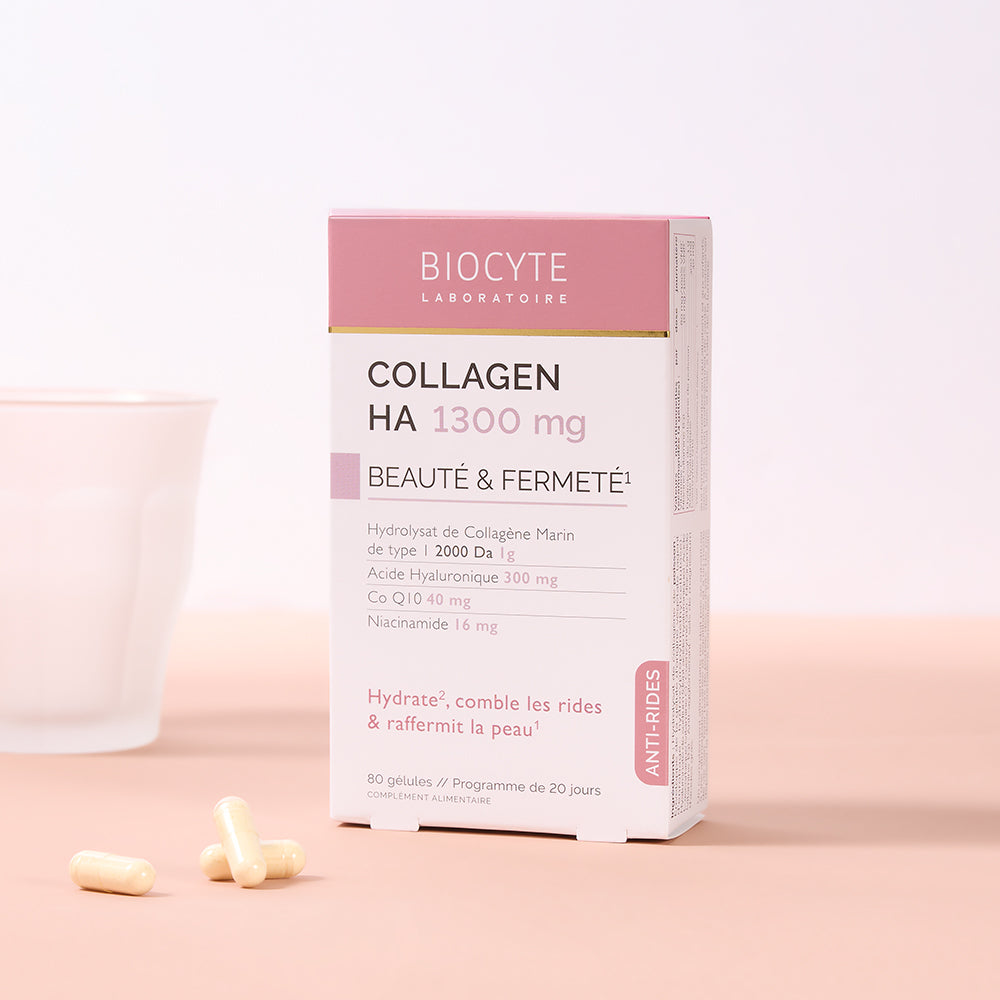
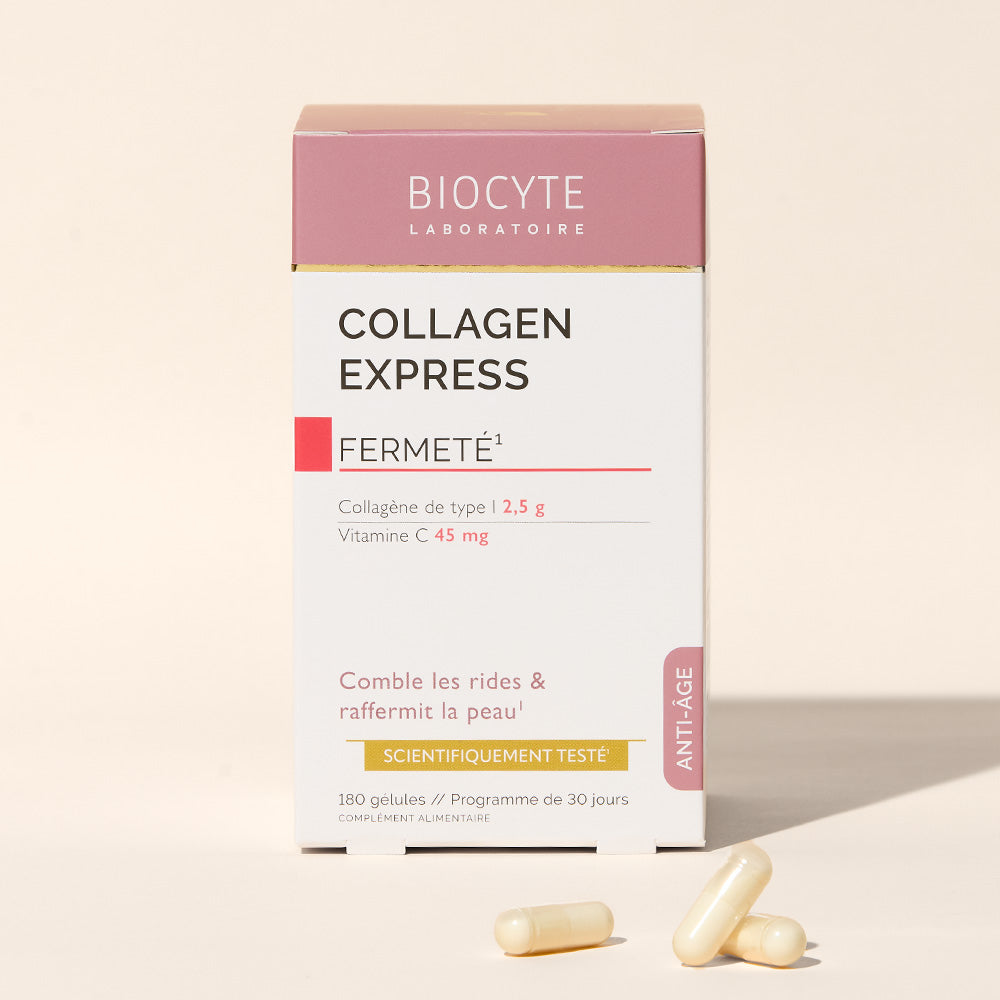
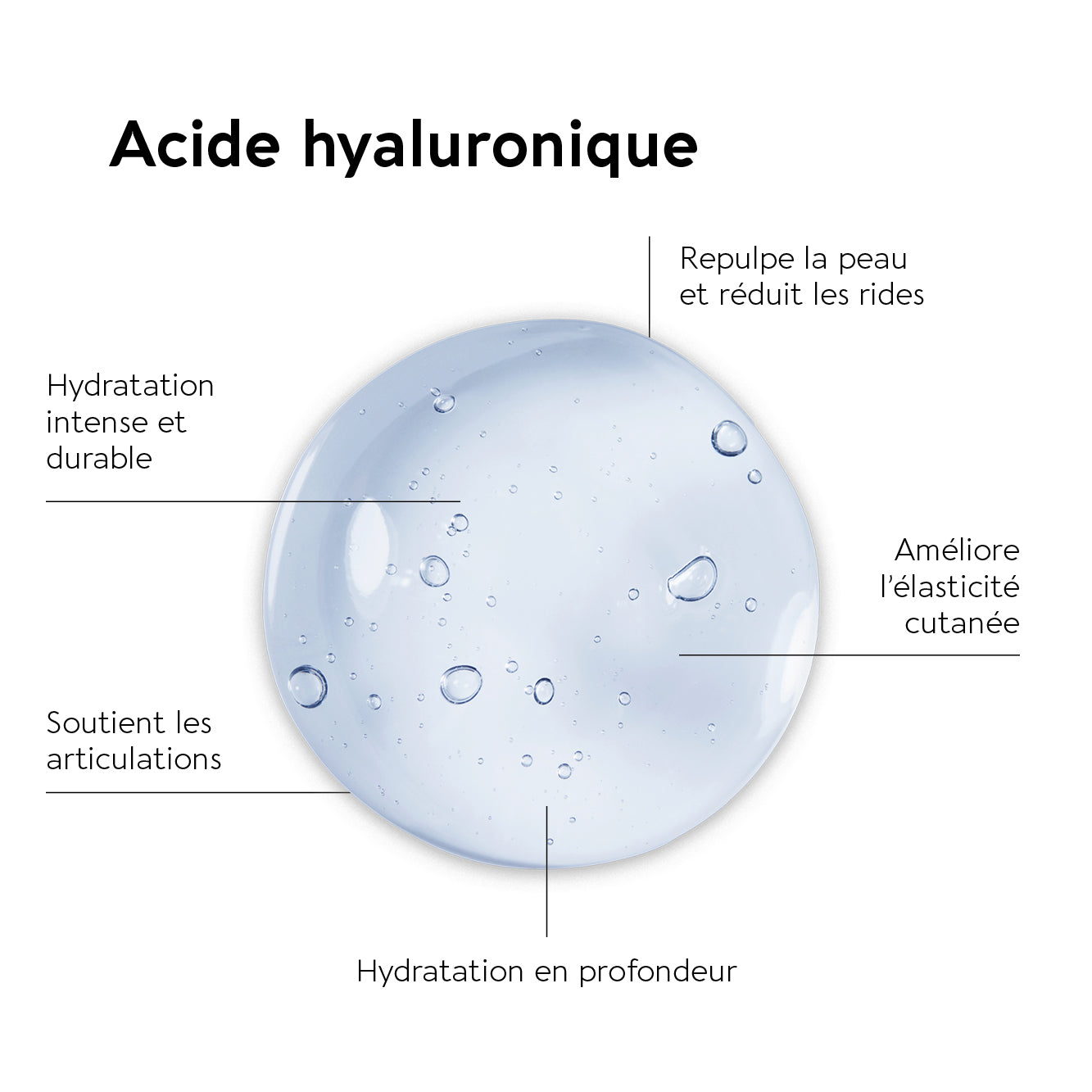
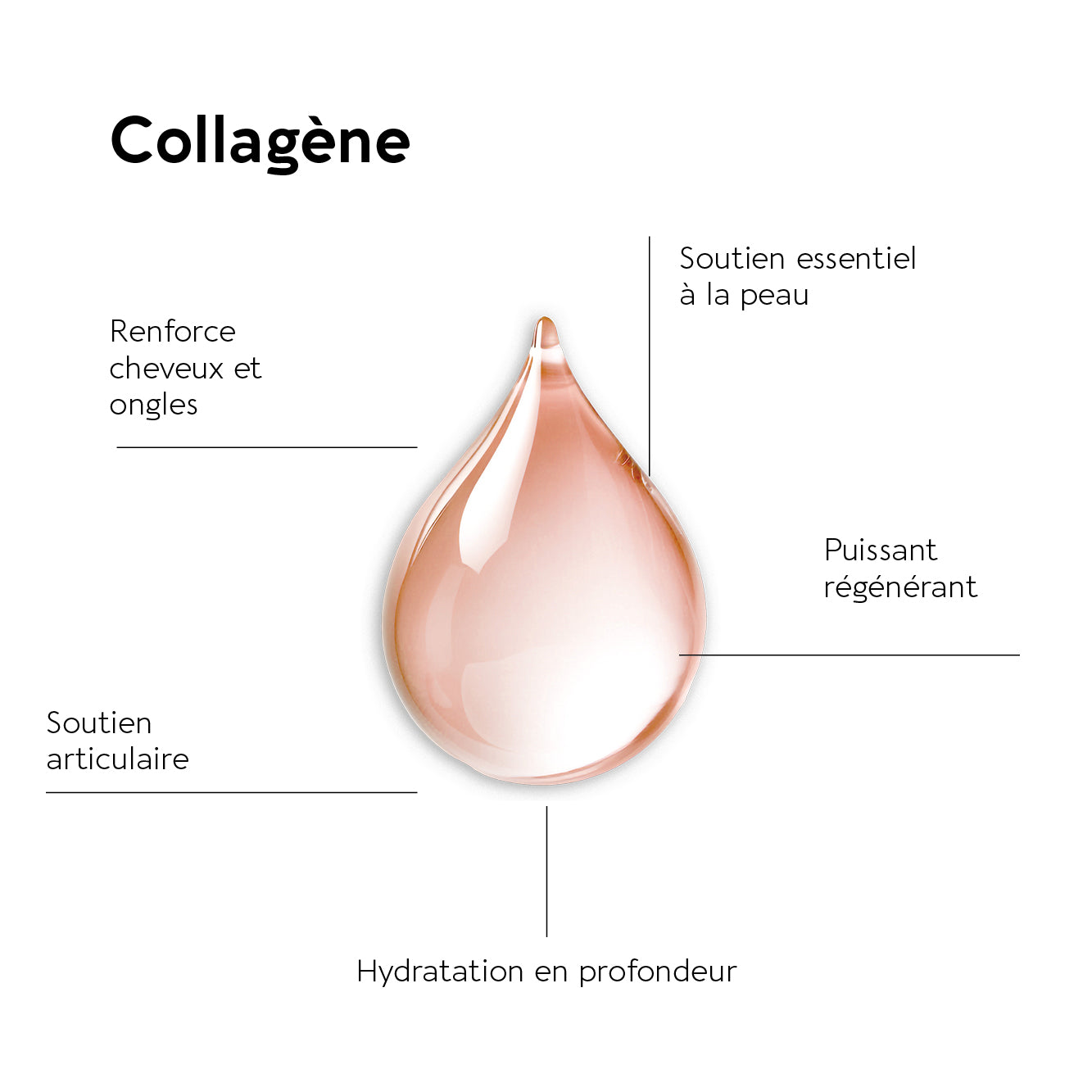
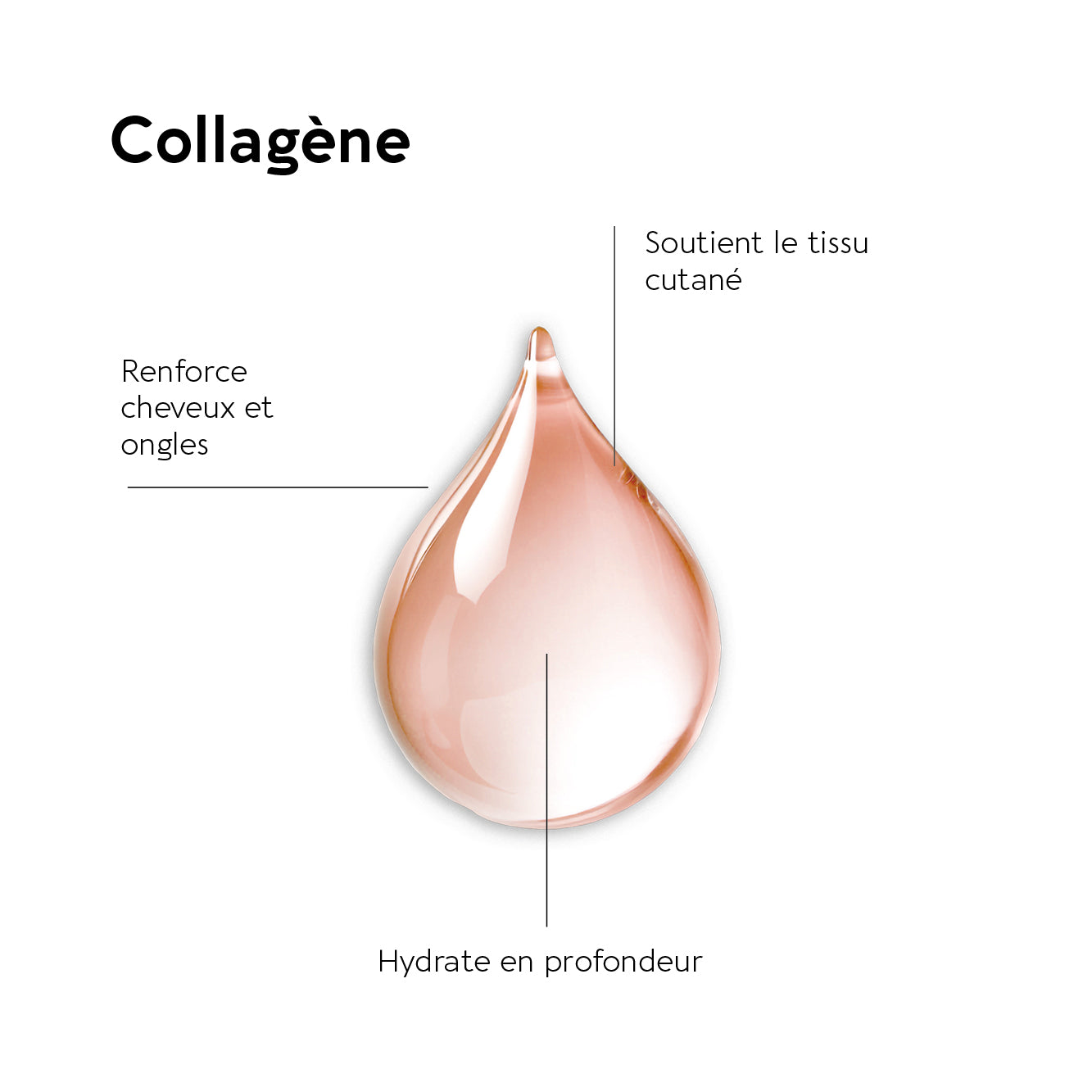
What is collagen?
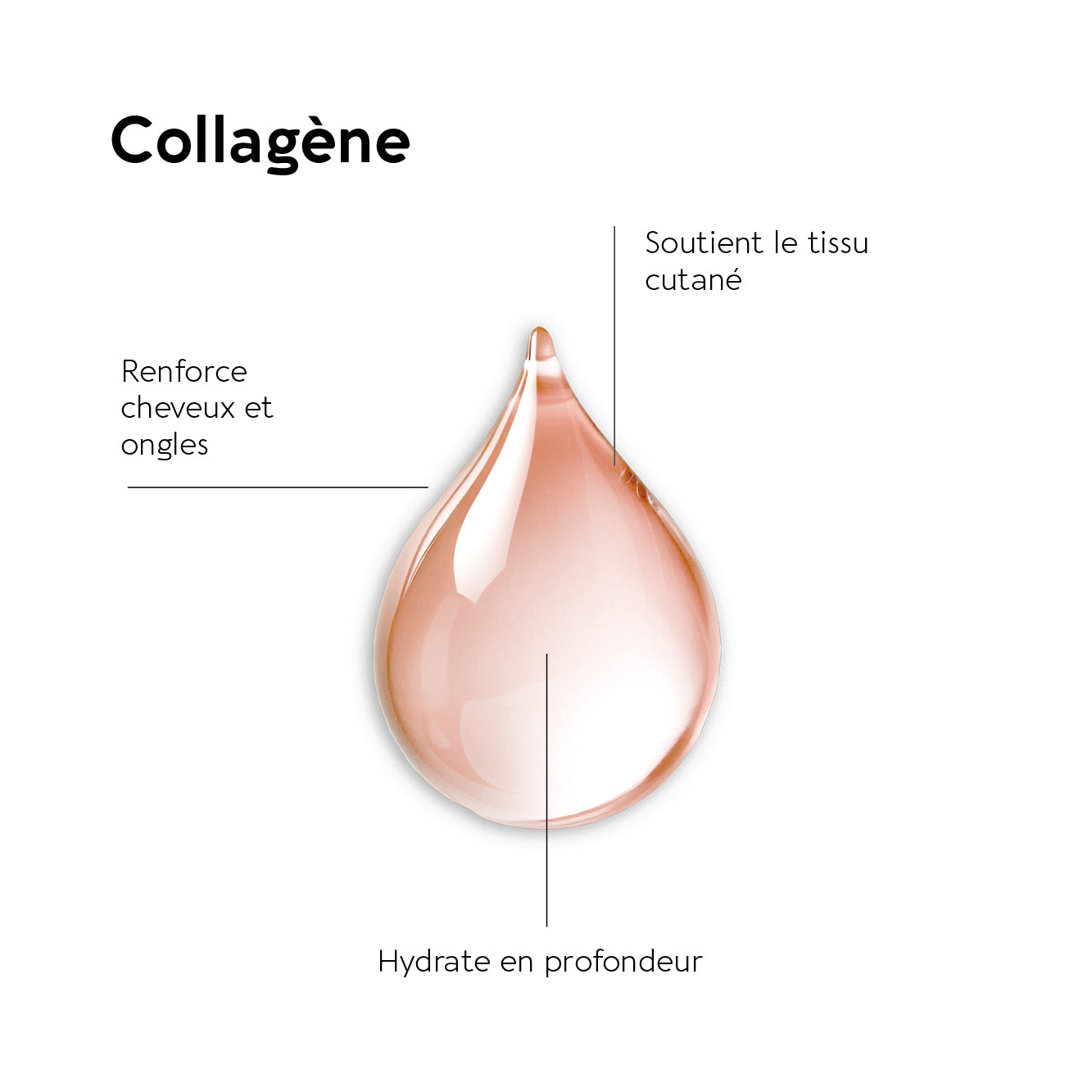
Collagen is a protein found in all body structures: skin, cartilage, joints, and connective tissues. Representing nearly 70% of our skin's weight, this protein is the most abundant in our bodies. Along with elastin and hyaluronic acid, collagen hydrolyzate is essential for maintaining skin strength and elasticity and aiding in tissue regeneration.
What are the different types of collagen?
There are more than 25 types of collagen produced by our body. The most important are collagen types I, II, and III, which together represent 80% of the collagen in our body:
- Type I collagen: it is the most abundant in the body and is found mainly in organs, skin, tendons and ligaments. It provides strength and elasticity to tissues. Type I collagen helps keep hair and nails strong; skin supple and helps the epidermis regain its shape after movement. There is also a specific range offood supplements for hair and nails.
- Type II collagen: It is located in hyaline cartilage. It forms fibrils and protects our joints by preventing friction between bones. A deficiency in type II collagen often leads to joint pain.
- Type III collagen: Found in the skin and organs. This collagen helps maintain skin hydration and muscle elasticity.
As with most proteins, collagen synthesis in our bodies decreases with age. Also, other factors can contribute to collagen loss: stress, pollution, lack of vitamin E, vitamin C and minerals, excessive sun exposure, etc. With Biocyte food supplements, it is possible to help the bodyboost collagen production to maintain beautiful skin and healthy joints.nutricosmetic active ingredientsact from the inside through intestinal assimilation to reach the bloodstream.
How to recognize a collagen deficiency?
Collagen is essential for the structure of the human body and skin health. Today, a deficiency manifests itself in early signs of aging, such as wrinkles around the eyes, wrinkled skin, and thinning hair. To remedy this, it is recommended to take a collagen treatment.
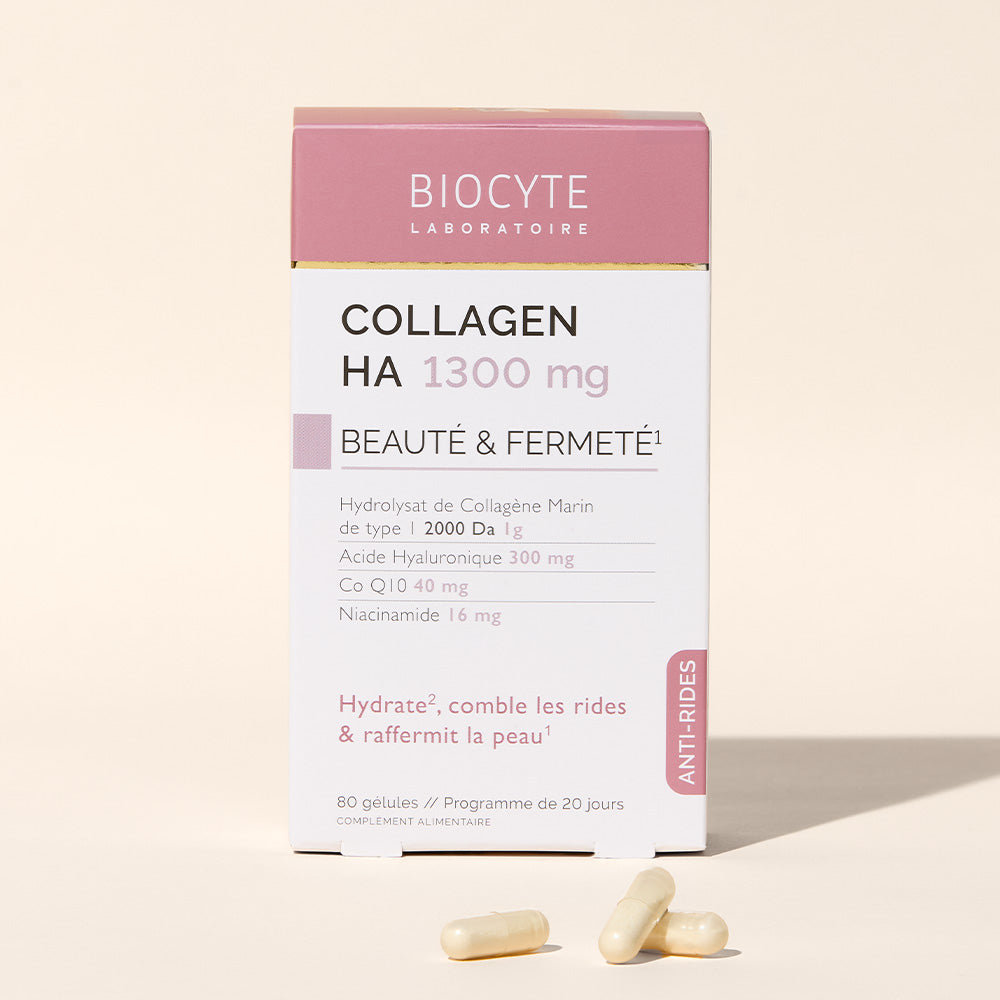
Taking collagen, particularly in the form of low-molecular-weight hydrolyzed marine collagen (often made in France), is an effective way to benefit from the effects of collagen. Incorporating these collagen-based products into a routine that combines a varied and balanced diet, regular physical activity, and a healthy lifestyle can help address these deficiencies. Some supplements, enriched with brewer's yeast, offer different types of collagen and act as a natural solution for consuming collagen.
How long does it take? Generally, a course of treatment over several months is enough to see significant improvements. It really works when you combine this supplement with a healthy lifestyle to maintain your health above all else.
The collagen food supplement for anti-aging and anti-wrinkle action
Collagen is the basic protein of our skin. Collagen fibers are located in the dermis, the inner part of the skin beneath the epidermis. They are organized and intertwined to provide strength and elasticity to the skin. Over time, the collagen fibers become fewer and disorganized. As a result, the skin loses elasticity, wrinkles form, and the epidermis becomes drier. Eventually, wrinkles become more pronounced, cheeks become hollow, and the skin loses its radiance. To remedy this, you can start usingsupplements to rejuvenate your faceand ofanti-aging food supplements.
Collagen, a key protein in the skin, plays a vital role in maintaining its youthfulness and elasticity. By naturally boosting its production, you canrejuvenate with collagen, thus promoting firmer and brighter skin.benefits of marine collagenare particularly noteworthy, as this form of collagen helps nourish and revitalize the skin, providing an effective solution to combat the signs of skin aging.
Collagen food supplement: impact on mobility and joint health
Our ligaments and cartilage are composed of 80% collagen. They play an essential role in joint health: ligaments connect bones together and provide strength and flexibility, while cartilage acts as a shock absorber, supporting each joint movement. As collagen levels decrease with age, joints lose their flexibility and stiffness develops. The risk of injury is higher, and daily life can be impacted by inflammatory pain.
Bioavailability of collagen peptides in dietary supplements
Bioactive collagen peptides are sequence-specific polypeptides capable of largely surviving digestive processes and crossing the intestinal barrier intact in order to exert their bioactivity on targeted tissues and organs.
Collagen peptides are very rich in proline amino acids, which form peptide bonds that are more resistant to enzymatic degradation. Collagen peptides absorbed orally (collagen drinks, collagen capsules, collagen sticks, etc.) can thus cross the gastric lumen and be assimilated at the intestinal level. It is this very specific structure of polypeptides that facilitates their transport through the intestinal villi.
Regarding its transport, collagen in the form of short chains of amino acids will easily cross the intestinal barrier through cellular junction points. This type of transport is called "paracellular transport." Once in the bloodstream, collagen peptides will be able to reach the various tissues, and thus exert their action on fibroblasts, the main cells responsible for collagen production.
Regarding its distribution, in vivo experiments indicate that orally administered collagen peptides are transferred to the skin and remain at a high level for 14 days. Collagen can then restart endogenous production through its action on fibroblasts, and peptides consisting of proline and hydroxyproline will strengthen the construction of collagen fibers and improve the structure of tissues and skin.
Link with other nutrients
It's crucial to understand that collagen doesn't work alone to keep your skin and joints healthy. It often works in conjunction with other vitamins and minerals for a synergistic effect. For example, vitamin C plays a vital role in collagen synthesis, facilitating the bonding of collagen molecules together for stronger, more elastic skin. Zinc and vitamin E also play a role in supporting collagen structure and protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Sources:
Borumand, M. & Sibilla, S. “Daily Consumption of the Collagen Supplement Pure Gold Collagen® Reduces Visible Signs of Aging,” Clinical Interventions in Aging, 2014.
Ricard-Blum, S. “The Collagen Family,” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2011.
Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, et al. “Collagen: The Fibrous Proteins of the Matrix,” in Molecular Cell Biology, 4th edition, 2000.
Avila Rodriguez, MI, et al. “Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications,” Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 2018.